| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- iOS배포
- 계산기앱
- 스프링
- Xib
- 앱배포
- iOS계산기
- 계산기앱만들기
- iOS앱배포
- AJAX
- Swift
- subscript
- MainScheduler
- Xcode
- customclass
- 앱버전구하기
- 웹
- spring
- 파이썬서버
- jQuery
- Python
- ios
- DispatchGroup
- 스위프트
- 맥
- JavaScript
- FileOwner
- 자바스크립트
- FLASK
- 개발기록
- 딩동말씀
- Today
- Total
개발하는 뚝딱이
컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2(6) 본문
Video streaming and content distribution networks (CDNs)
Internet Video
- video tarffic : major consumer of Internet bandwidth
- Netflix, Youtube : 37%, 16% of downstream residential ISP traffic
- ~ 1B YouTube users, ~ 75M Netflix users
- challenge
- scalibility - single mega-video server won't work
- heterogenity
- different users have different capabilities (e.g., wired versus mobile; bandwidth rich vershs bandwidth poor)
- solution : distributed, application-level infrastructure
Video encoding
- video : sequence of imags displayed at constant rate (e.g., 24 or 30 frames/sec)
- digital image : array of pixels
- coding : use redundancy within and between images to decrease number of bits encode image
- spatial (within image) - 인접한 pixel 간의 압축
- temporal (from one image to next) - frame 사이의 pixel간에 압축 이용
Video Encoding
- CBR (constant bit rate) : video encoding rate fixed
- VBR (variable bit rate) : video encoding rate changes as amount of spatial, temporal coding changes (압축 더 많이 할 수 있을 때는 더 함)
- examples:
- MPEG 1 (CD-ROM) 1.5Mbps
- MPEG2 (DVD) 3-6Mbps
- MPEG4 (often used in Internet, < 1Mbps)
Streaming multimedia
- Traditional streaming service
- Based on RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol) [RTP, RTSP]
- Complex : burden to a server
- 요즘 - UTP (UDP 기반)
- Session management and flow control
- Streaming over HTTP - (GET으로 받음) TCP 기반

한꺼번에 왕창받으면 bufferr가 많이 필요하다.
그러나 사용자들이 도중에 많이 중단하는데 이는 bandwidth낭비가 된다.

Progressive Downloading : 일부 chunk만 요구. play하다가 또 chunk를 요구한다.
이는 일부 bandwidth만 낭비한다.
Streaming multimedia : DASH
- DASH : Dynamic, Adaptive Streaming over HTTP
- DASH로 heterognity 해결!
- server :
- divides video file into multiple chunks
- each chunk stored, encoded at different rates - 압축을 고화질/저화질... 다양한 옵션이 가능
- manifest file : provide URLs for different chunks - 어떤 rate를 가진 url이 무엇인지 기록
- client:
- first requests the manifest file - MPEG에서는 MPD(Media Presentation Description)
- periodically measures server-to-client bandwidth
- consulting the manifest, requests one chunk at a time
- choose maximum coding rate sustainable given current bandwidth (현재 availble한 bandwidth에 따라 chunk 요청)
- can choose different coding rates at different points in time (depending on available bandwidth at time) - 화질이 나빠질 수는 있으나 끊기지 않는다!
Streaming multimedia : DASH
"inteligence" at client : client determines
- 언제 chunk를 요구할 것인가 (buffer starvation, or overflow does not occur)
- 어떤 encoding rate를 요구할 것인가 (higher quality when more bandwidth available)
- 어디서 chunk를 요구할 것인가 (can request from URL server that is "close" to client or has high available bandwidth)

Content Distribution Networks(CDNs)
Challenge : 사용자가 너무 많다
Option 1 : single, large "mega-server"
- single point of failure (centralized 단점)
- point of network congestion
- long path to distnat clients - the average end-to-end BW 보장되어야 하는데 bottleneck 발생
- multiple copies of video sent over outgoing link - 인기많은 비디오라서 동일한 traffic이 반복하여 link를 통해 전달될 수 있다. 가는 길이 겹쳐서 congestion 발생
- this solution doesn't scale
Opetion2 : store/serve multiple copies of videos of multiple geographically distributed sites (CDN)
- Enter deep : CDN 서버를 사용자와 가능한 가까이 설치
- used by Akamai, 1700 locations
- Bring home : access networ 근방 POP에 큰 용량의 cluster를 smaller number(10's)만큼 설치하겠다
- used by Limelight
CDNs which content is retrieved
- CDN : stores copies of content at CDN nodes
- 여러 서버에 분산시켜 두고, original server에 manifest file을 기록한다.
- e.g. Netflix stores copies of MadMen
- subscriber requests content from CDN
- 사용자 근처에서 content를 고르거나
- 만약 그 길이 traffic이 많으면 다른 것을 고른다

OTT challenges : coping with a congested Internet
- from which CDN node to retrieve content?
- viewer behavior in presence of congestion?
- what content to place in which CDN node?
- Over the top (OTT)
- A term used to refer to content providers that distribute streaming media as a standalone product directly to viewers over the Internet, by passing telecommunications, multichannel televison, and broadcast television platforms that traditionally act as a controller or distributor of such content.

CDN Content Access : a closer look
Bob(client) requests video http://netcinema.com/6Y7B23V
video stored in CDN at http://KingCDN.com/NetC6Y&B23V
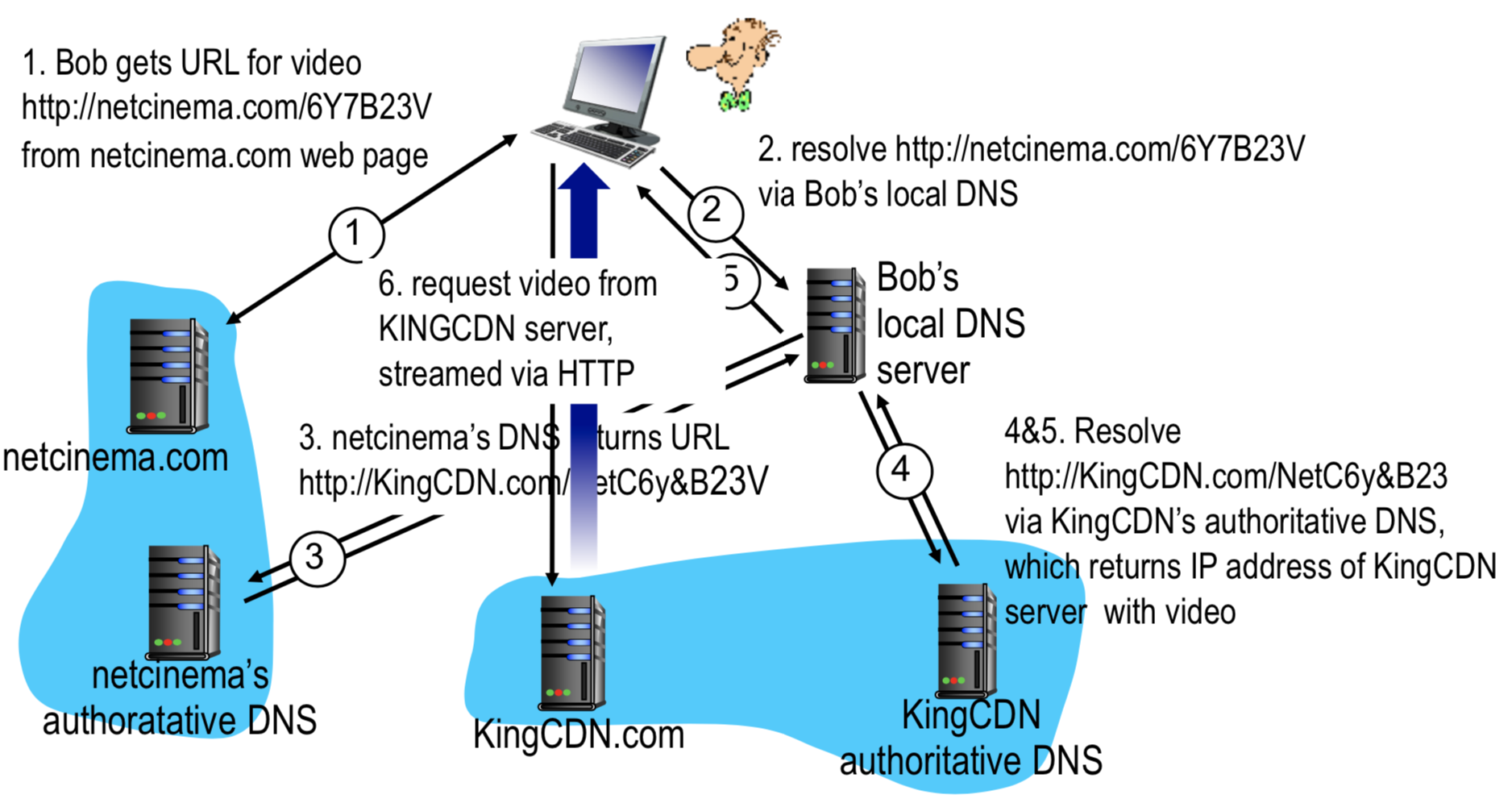
2번에서 netcinema.com/6Y7B23V에 대한 IP주소 요청
redirection하여 가까운 쪽 서버에서 받아가도록 한다.
CDN Content Access : Netflix

- No DNS redirection
- Push caching : CDN서버에 어떤 영화를 둘 것인가! 어떤 지역에서, 지역 사람들이 특정 영화를 많이 본다고 할 때 이를 예측하여 traffic이 적을 때, 미리 영화를 server에 넘겨둠
CDN Content Access : Youtube
- 구글이 인수
- Use its private CDN to distribute YouTube Video
- Use DNS redirection : redirection 시킬 때, node selection algorithm으로 RTT(거리 traffic) 측정함 (load balance)
- Use push caching ; 자기 가까운 쪽에 요청하면 가까운 쪽 서버에 요청. 그 서버에 없으면 original server에서 받음 (마치 web cache와 비슷)
- MPEG-DASH 알고리듬
- HTTP streaming with no adaptive streaming
- The user manually selects a video version
- Currently using MPEG-DASH
- Cluster selection strategy
- Selects a cluster which has the lowest RTT while considering the load balance
- Kankan : 처음엔 P2P이지만, P2P로만 받을 때 문제가 생기면 CDN을 취한다.
- Originally based on P2P, migrated to a hybrid CDN-P2P
'컴퓨터 네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch1(6) (0) | 2019.10.15 |
|---|---|
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch1(4) (1) | 2019.10.15 |
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2(5) (0) | 2019.10.09 |
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2(4) (0) | 2019.10.09 |
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2(3) (0) | 2019.10.08 |




