Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- iOS배포
- 앱배포
- spring
- 딩동말씀
- DispatchGroup
- 맥
- iOS앱배포
- Python
- ios
- 계산기앱만들기
- 스위프트
- FLASK
- 웹
- 스프링
- Xcode
- 파이썬서버
- Swift
- 개발기록
- 앱버전구하기
- MainScheduler
- JavaScript
- Xib
- 계산기앱
- subscript
- 자바스크립트
- jQuery
- AJAX
- FileOwner
- iOS계산기
- customclass
Archives
- Today
- Total
개발하는 뚝딱이
컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2(4) 본문
DNS
DNS : Domain Name System
- Name & Addres
- Name
- Character string for human use e.g. www.naver.com
- Mnemonic
- Address : Where you are
- IP address (32 bit string) : used by a machine
- www.naver.com → 32-bit string으로 변환
- Name
How to map between IP addresses and name?
Mapping a name to an address or an address to a name is called name-address resolution.
DNS
- Name resolution
- Solution 1 : Static Mapping
- Hostname을 file 또는 host file을 이용하여 주소를 mapping시킨다.
- 그러나 파일의 양이 많아져서 더 이상 사용하지 않는다
- Solution 2 : Dynamic Mapping(DNS)
- The internet has too many objects for a single management center
- uses Distributed Database system
- Scalabitlity, maintenance
- 현존하는 세계 최대 D-DB
- Partition the name space into a hierarchicla tree
- Domain hierarchy
- Partition the name space into a hierarchicla tree
- Solution 1 : Static Mapping
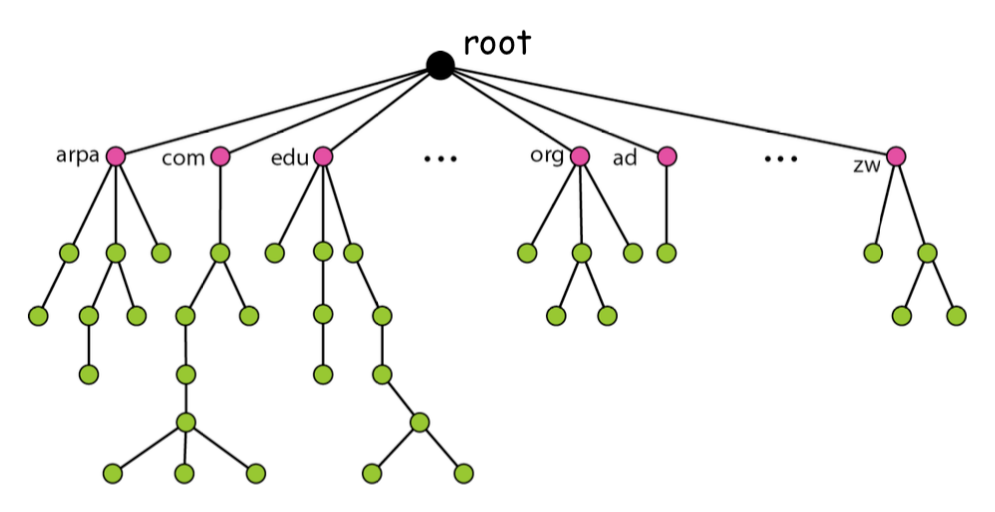
- The tree can have only 128 levels
- level 0 (root) to level 127
- www.example.com (.으로 연결해서 사실 127개까지 내려갈 수 있음)
- In the Internet, the domain name space(tree) is divided into three different sections:
- generic domains [ .net .edu .org ]
- country domains [ .kr ]
- inverse domain : IP는 아는데 nemonic을 모를 때 사용되는 도메인
- 203.252.97.22 → 22.97.252.203.in-addr.arpa
Overview of DNS

Client wants IP for www.amaz.on.com
- client는 root server에게 com DNS server를 요청한다
- client는 DNS 서버로부터 amazon.com DNS server를 묻는다
- client는 amazon.com DNS 서버로부터 www.amazon.com의 IP주소를 얻는다
13 root servers (A-M) in the Internet
- www.root-servers.org
- Each server is actually a cluster of replicated servers (한 대가 아니라 server farm)
TOP-level Domain (TLD) servers
- Responsible for com, org, net, edu, etc, and all top-level country domains uk, fr, ca, jp.
Authoritative DNS servers
- 단체에 대한 DNS
- organization's DNS servers, providing authoritative hostname to IP mappings for organization's servers
- Can be maintained by organization or service provider

.kr DNS
- 6 .KR name servers
- Primary : operated by KRNIC
- Secondary : 5 servers by 4 organizers

Local Name Server
- 반드시 설정해줘야 함
- does not strictly belong to hierarchy
- Each ISP (residential ISP, company, university) has one "Local Name Server"
- Also called "default name server"
- When a host makes a DNS query, query is sent to its local DNS server
- acts as proxy, forwards query into hierarchy
Name Resolution : Iterative Queries
- Example:
- Host at cis.poly.edu wants IP address for gaia.cs.umass.edu
- Iterative queries
- contacted server replies with name of server to contact
- "I don't know this name, but ask this server"
- Typical method

Name Resolution : Recursive Queries
- recursive query :
- puts burden of name resolution on contacted name server
- heavy load at upper levels of hierarchy

DNS Caching and Update Recoreds
- once (any) name server learns mapping, it caches mapping
- TTL만큼의 시간이 지나면, cache entries는 없어진다.
- TLD 서버를 local name 서버에 캐시로 저장한다.
- 그래서 root name server를 방문하지 않아도 될 수 있다.
- cached entries may be out-of-date (best effort name-to-address translation!)
- if name host changes IP address, may not be known Internet-wide until all TTLs expire
- update/notify mechanisms propsosed IETF standard(변경되면 알려주는 기능 O)
- RFC 2136
Services Provided by DNS
- DNS
- DNS can use the services of UDP or TCP using the well-known port 53
- UDP가 주로 사용되는데 overhead를 줄이기 위해서이다. 에러가 나면 IP에서 그냥 버리고 time out되면 다시 요청하면 된다.
- TCP는 connection-oriented이며, connect와 release로 overhead가 발생한다
- DNS identify objects on the Internet
- Host name
- Canonical hostname (원래 자기이름)
- Alias hostnames (별명)
- Name server (해당하는 도메인의 A.S)
- Mail server
- Information
- Host name
DNS records
DNS : distributed db storing resource records (RR)
RR format : (name, ttl, class, type, value)
- Type : Specifies the types of the value
- A: name = host, value = IPv4 address
- NS (Name Server) : name = domain name, value = IP address of authoritative name server for this domian
- CNAME : name = alias name, value = Canonical name
- MX (Mail Server) : name = alias hostname, value = name of mailserver associated with name
- HINFO : host information (CPU and OS)
- TXT : text (uninterpreted ascii text)
- TTL : [Time To Live] how long the resource reocord is valid. cache에서 언제 살아질 것인가
DNS recrods: Example

DNS Messages
Query and reply messages have the same format
message header
identifiaction : 16 bit numbers for query, reply to query users same numbers
flags :
- query or reply
- recursion desired
- recursion available
- reply is authoritative

Inserting records into DNS
- How are new domains added to DNS?
- This done through a registrar, a commercial entity accredited by ICANN.
- A registrar first verifies that the requested domain name is unique and then enters it into the DNS database.
- Need to provide registrar with names and IP addresses of your authoritative name server (primary and secondary)
- Registrar inserts two RRs into the com TLD server
- A fee is charged.
Accredited Registrar in KOREA

'컴퓨터 네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2(6) (0) | 2019.10.10 |
|---|---|
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2(5) (0) | 2019.10.09 |
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2(3) (0) | 2019.10.08 |
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2 (2) (0) | 2019.10.08 |
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2(1) (0) | 2019.09.27 |




