| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- Xib
- 앱버전구하기
- ios
- FLASK
- 맥
- customclass
- 자바스크립트
- DispatchGroup
- 계산기앱만들기
- jQuery
- 개발기록
- 스위프트
- iOS계산기
- Xcode
- iOS앱배포
- MainScheduler
- spring
- subscript
- 스프링
- 계산기앱
- 파이썬서버
- 딩동말씀
- iOS배포
- Swift
- 앱배포
- Python
- JavaScript
- AJAX
- FileOwner
- 웹
- Today
- Total
개발하는 뚝딱이
컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2 (2) 본문
Application layer ; Web and HTTP
Web and HTTP
- web page consists of objects
- object can be HTML file, JPEG image, Java applet, audio file...
- web page consists of base HTML-file which includes several referenced objects
- Hypertext/hypermedia file which information is organized as a set of documents (objects) ; object들을 포함한 document
- Each object is addressed by a uniform resource locator (URL)

HyperText Transfer Protocol overview
- Web's application layer protocol
- web client가 web server에게 pages를 요청하는 방법, server가 client에게 pages를 전달하는 방법
- Client/Server model
- client : browser that requests, receives, (using HTTP protocol) and "displays" Web objects
- server : Web server sends (using HTTP protocol) objects in response to requests
- HTTP is stateless protocol
- The server maintains no information of previous requests from the same client
- HTTP uses TCP as its underlying transport protocol
- TCP로 reliable한 서비스 제공 - 데이터 loss 없이 전달
- The well-known port number for HTTP is 80
- 다른 port number를 쓰고 싶으면 ex) www.example.com:8080
- HTTP-TCP connection can be non-persistent or persistent
- HTTP 1.0:RFC 1945, HTTP1.1:RFC 2068 (in 1998)
- HTTP 2.0:RFC 7540 (2016)
HTTP connections
- Non-persistent HTTP
- TCP connection으로 많아야 하나의 object를 보낸다
- HTTP/1.0 uses non-persistent
- 하지만! TCP connection을 병렬로 하여 object를 더 많이 보낼 수 있다. -> 응답시간이 줄어들 수 있으나 -> 서버의 부담이 커진다
- Persistent HTTP
- client와 서버 사이에 single TCP connection으로 여러 object를 보낼 수 있다
- server leaves connection open after sending response
- subsequent HTTP messages between the same client/server are sent over the same connection
- HTTP/1.1 uses persistent connections in default mode
- client와 서버 사이에 single TCP connection으로 여러 object를 보낼 수 있다
Non-Persistent HTTP connections

TCP 3-way handshaking ; connection set-up 또는 release할 때
First handshake (reuqest)
Second handshake(response)
Third handshake + request(acknowledgement)
그림과 같이, file과 image를 parallel하게 진행할 수 있다
Persistent HTTP Connections

TCP 3-way handshaking으로 setup 요청
request와 response를 모두 끝내고 release한다
Persistent without pipelining
- client issues new reuqest only when previous response has been received
- one RTT for each referenced object (요청한 정보양이 적으면 RTT-round trip time마다 하나의 object를 받게 됨)
Persistent with pipelining
- default in HTTP/1.1 - 그러나 실질적으로 사용X
- client sends requests as soon as it encounters a referenced object
- as little as one RTT for all the referenced objects

HTTP Message
two types of HTTP messages : request, response
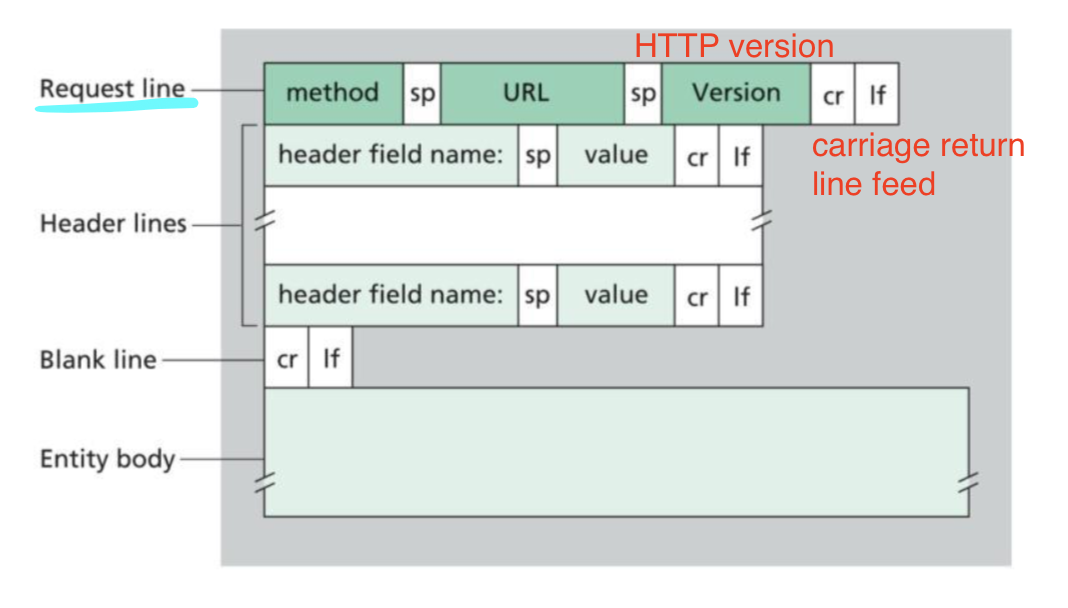
HTTP Request Message
HTTP request message: ASCII (사람이 읽을 수 있다)

Methods of Request line in a request message

HTTP는 RESTful한 구조이다
RESTful? 웹의 장점을 최대한 활용할 수 있는 아키텍쳐
CRUD ; Create + Read + Update + Delete ( + Notification) // POST + GET + PUT + DELETE
Header names of Request line in a request message
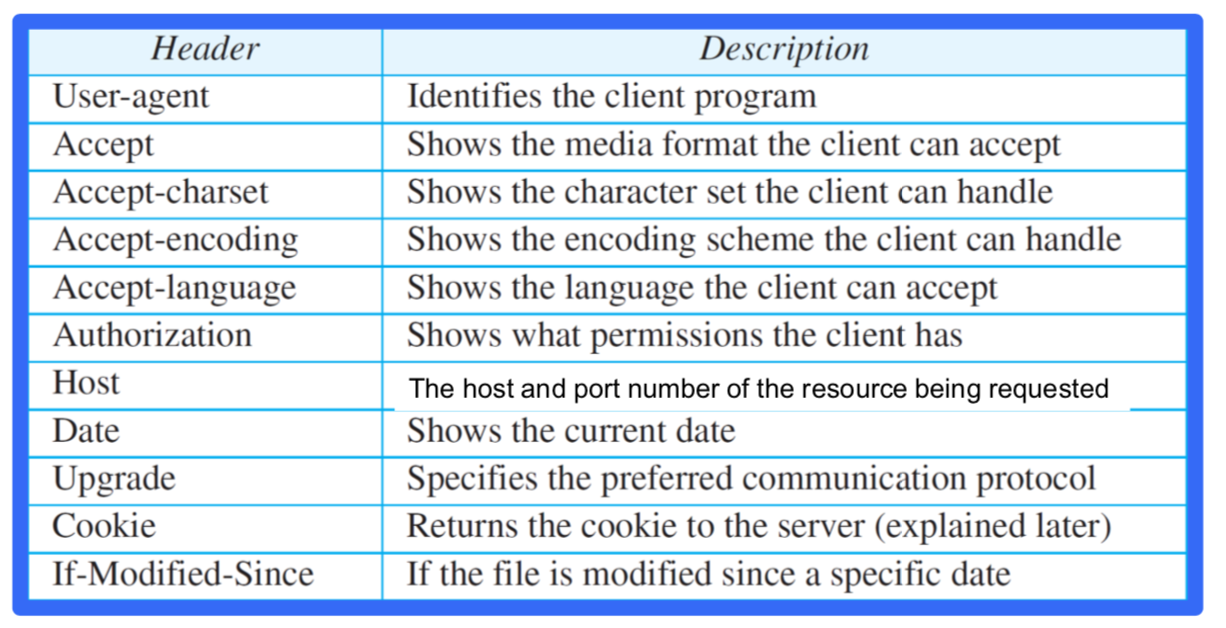
User-agent : 사용하는 웹 부라우저가 어떤 스타일인가
Accept-language / Host / Cookie ; stateless를 보완하기 위해
Uploading form of input
- POST method:
- Web page often includes form input
- Input is uploaded to server ; parameter로 맞는 것을 요청할 때 server로 날라감
- 보통 과거에 POST를 이용하였으며, request의 body에 들어감
- URL method:
- uses GET method
- Input is uploaded in URL field

HTTP Response Message


Status code in Response Message
- 3-digit integer가 받은 request에 대한 응답을 알려준다
- Status phrase가 status code에 대한 짧은 text형식의 설명을 준다
- 1XX : informational
- 200 OK : request succeeded, information returned
- 3XX : Redirection
- 301 Moved Permanently : requested object moved, new location specified later in this message (Location:)
- 400번대 : Client error
- 400 Bad Request : Syntax eroor in request
- 404 Not Found : requested document does not exist on this erver
- 500번대 : Server error
- 505 Version Not Supported
HTTP Response Message
Header names in Response Message

telnet : terminal emulation program (default가 23번)
User-server state : cookies
- HTTP is a stateless protocol
- Server forgets about each client as soon as it sends response
- Issue to stateless behavior
- When a web site wants to identify users
- When the server wishes to restrict user access
- When the server wants to serve content as a function of the user identity
- Cookie technology
- When a server identifies a new user, it adds Set-cookie header to its response, containing an identifier for that user.
- The client is expected to store the info from the Set-cookie header on tis disk, and use it in all subsequent requests made to the same server.
- A cookie is a short piece of data, not an executable code, and can not directly harm the machine.
- Four components of cookie
- set-cookie header line in the HTTP response message
- cookie header line in HTTP request message
- cookie file kept on user's host and managed by user's browser
- back-end database at Web site
- Problem in privacy
Cookies:keeping "state"
Example : interaction with Amazon

Web caches (proxy server)
- Web cache / Proxy server
- An intermediary entity that satisfies HTTP requests on the behalf of an origin Web server
- User browsers must be configured so that all requests are first directed to its Web cache
- object in cache : cache returns object
- Else cache requests object from origin server, then returns object to client

- Advantages
- Reduce Response time for client request
- Reduce traffic on an institution's access link (특정 단체의 access link traffic을 줄일 수 있다)
- Disadvantages
- Proxy server가 cached object를 갖고 있지 않는 경우, proxy server를 거쳐 origin server, proxy server를 거쳐야 한다. 이는 직접 요청하는 것보다 효율이 떨어지며 overhead가 발생할 수 있다
Caching example
Assumptions
- average object size = 100k bits
- avg. request rate from institution's browsers to origin servers = 15/sec
- delay from ISP access router to any origin server and back to router = 2sec
Consequences
- utilization on LAN = 1.5%
초당 total 요청량 = 15/sec * 100k = 1500k/sec = 1.5M/sec
→ LAN에서 100M → 1.5M/100M →1.5%
- utilization on access link = 99%
1.5M/1.54M → 99%
Total delay = Internet delay + access delay + LAN delay
= 2sec + minutes(올 때) + miliseconds

Possible solution
increase bandwidth of access link to 10Mbps
Consequences
utilization on LAN = 1.5%
utilization on access link = 15%
Total delay = Internet delay + access delay(msec) + LAN delay(msecs)
often a costly upgrade

Install cache
suppose hit rate is 4 (요청한게 proxy에 있을 확률 40%)
Consequence
- 40% requests will be satisfied almost immediately
- 60% requests satisfied by origin server
- utilization of access link reduced delays (say 10 msec)
- total avg. delay = 0.4*(LAN access delay) + 0.6*(WLAN access delay) = 0.4*(~msec) + 0.6*(2+0.01) = ~1.2 secs

Web Cache Challenge
Problem : an object in the cache might be stale ; origin server의 정보가 업데이트되면?
Goal : cache가 old version이면 object를 보내지 않는다
Solution : conditional GET
- Use If-Modified-Since header line
- Cache will include requested object in response only if object has been modified since the specified date

- Pull caching : 요청했을 때만 보냄
- Push caching : 요청을 안했을 때도 보냄 ex)kakao
'컴퓨터 네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2(4) (0) | 2019.10.09 |
|---|---|
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2(3) (0) | 2019.10.08 |
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch2(1) (0) | 2019.09.27 |
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch1 (3) (0) | 2019.09.25 |
| 컴퓨터 네트워크 ch1 (2) (0) | 2019.08.29 |




